Towards the end of January 2022, the Office of Management and Budget (OMB) released its memorandum on moving government agencies to a zero-trust model. Enterprises that align themselves to industries regulated by the federal agencies can take a cue from it to improve their security posture. The memo considers the recent ransomware attacks on various… Continue reading Cues from OMB Zero Trust Architecture memo
Category: Risk Management
Security Management Practices
Machine Learning, Society and Cybersecurity
Machine Learning (ML) appears to have made great strides in many areas, including machine translation, autonomous vehicle control, image classification, enabling games on Xbox, PlayStation, Nintendo, and Steam. This has made Artificial Intelligence popular and securing the information in it is challenging. Let’s take a look at an industry that many of us use. We… Continue reading Machine Learning, Society and Cybersecurity
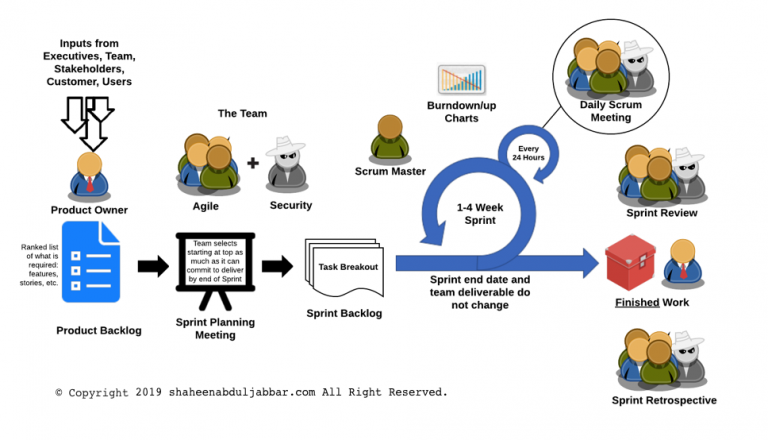
Security in Agile Methodology
Many large organizations are moving towards the Agile software development lifecycle (SDLC) methodology. Agile methodology is a combination of iterative and incremental process models with a focus on process adaptability and customer satisfaction by rapid delivery of working software product. The general characteristics of any Agile methodology are: Prioritizing feedback. Agile teams rely heavily on the… Continue reading Security in Agile Methodology
Information Security Risk Analysis (ISRA)
The ISRA methodology is used by a system designer, manager, or security analyst to identify security concerns, develop an action plan, analyze costs, and assign responsibilities. The process allows a facilitator to perform a subjective risk assessment on a particular system, application, or other corporate assets. The ISRA involves the system users from the very… Continue reading Information Security Risk Analysis (ISRA)
Facilitated Risk Analysis and Assessment Process (FRAAP)
FRAAP is a structured approach to an accelerated assessment of each component of a system within a short timeframe. It is consistent with the National Institute of Standards and Technology October 2001 Special Publication “Risk Management Guide of Information Technology Systems” and the FFIEC December 2002 “Information Security Risk Assessment.” The approach allows us to… Continue reading Facilitated Risk Analysis and Assessment Process (FRAAP)